Roman Empire Trade Routes : Uttarapath And Dakshinapath The Great Trade Routes Of Jambudwipa : By the end of the first century b.c., there was a great expansion of international trade involving five contiguous powers:
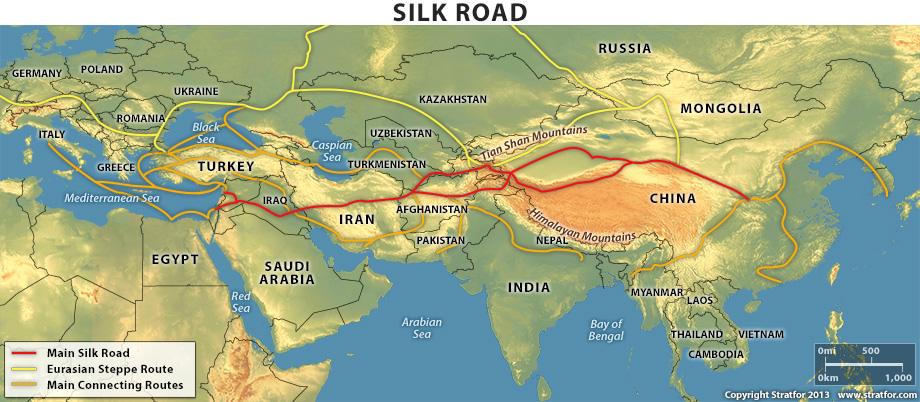
Roman Empire Trade Routes : Uttarapath And Dakshinapath The Great Trade Routes Of Jambudwipa : By the end of the first century b.c., there was a great expansion of international trade involving five contiguous powers:. The silk road is actually many routes from the roman empire through the steppes, mountains, and deserts of central asia and india to china. During the end of the third century, new amber trade routes heading east were started. Grain, olive oil, slaves, wine, metals, textiles and wild animals. This map gives information about the roman's road system throughout the empire and its primary maritime trading routes between the busiest and largest port cities within the empire. A guide to using a map of the ancient roman empire.
There were sea routes that covered the mediterranean and black seas and numerous land routes using the roads built by the romans. Trade routes covered the roman empire along with sea routes covering the mediterranean and black seas, and many different land routes which used the roads that the romans trade had built. Trade and moving the roman army around were the two principle reasons for building roads. First published in 1926, this book provides an outline of roman economic life during the first two centuries of the empire. Opaque amber, on the other hand, was made into incense.
Grain, olive oil, slaves, wine, metals, textiles and wild animals.
This map shows the major sources of trade goods in the roman empire, circa 200 ce.the map shows the sources of the following trade goods: A guide to using a map of the ancient roman empire. The language and the legions were supported by trade while being at the same time part of its backbone. Trade routes roman trade was the engine that drove the roman economy of the late republic and the early empire. Opaque amber, on the other hand, was made into incense. Trade and moving the roman army around were the two principle reasons for building roads. By the end of the first century b.c., there was a great expansion of international trade involving five contiguous powers: Trade routes and cities in europe from rome to the middle ages; Each chapter focuses on a different section of the roman sphere of influence, including trade routes to china and india, the goods native to various areas, and the means by which they communicated and traded with rome. The syrian desert, which would have seriously affected the trade routes. On the continent, the roman empire with it's single currency was spreading and occupied countries all adopted the roman monetary system as their. First published in 1926, this book provides an outline of roman economic life during the first two centuries of the empire. Amber was packed in intermediate points before being transported for the roman empire.
These regions were linked to rome by sea and overland routes along two main axes that are still important traffic and trade arteries today: Eastern empires traded for roman gold, among other items. Principal roman trade routes, internal and external in 180ad the forum cuppedinis in ancient rome was a market which offered general goods. The roman empire and the kushan empire (which ruled territory in. At least four other large markets specialized in specific goods such as cattle, wine, fish and herbs and vegetables, but the roman forum drew the bulk of the traffic.
Used by the romans was known as a corbitas.
The two main motives for building roads was trade and moving of the roman army. This map shows the major sources of trade goods in the roman empire, circa 200 ce.the map shows the sources of the following trade goods: All roads lead to rome. There were sea routes that covered the mediterranean and black seas and numerous land routes using the roads built by the romans. Trade routes roman trade was the engine that drove the roman economy of the late republic and the early empire. Further chapters examine the development of palmyra as a leading caravan. The roman empire, the parthian empire, the kushan empire, the nomadic confederation of the xiongnu, and the han empire.although travel was arduous and knowledge of geography imperfect, numerous contacts were forged as these empires expanded—spreading ideas, beliefs, and. Roman trade routes map (orbis, stanford uni) in addition to the 80,000 kilometres of first class roads (as at c. At least four other large markets specialized in specific goods such as cattle, wine, fish and herbs and vegetables, but the roman forum drew the bulk of the traffic. The province of hispania occupied a similarly important position as a source of food. Roman trade routes goods were continually transported throughout the roman empire. The language and the legions were supported by trade while being at the same time part of its backbone. Used by the romans was known as a corbitas.
Themost effective way to transport goods was by sea. The romans were able to establish trade routes throughout europe, asia, and africa. The roman empire, the parthian empire, the kushan empire, the nomadic confederation of the xiongnu, and the han empire.although travel was arduous and knowledge of geography imperfect, numerous contacts were forged as these empires expanded—spreading ideas, beliefs, and. Ad 200) built primarily for the movement of military forces, used by the imperial courier service, for government administration and lastly for trade, sea routes crossed the empire through the mediterranean from spain, france and. All roads lead to rome.

Trade routes of the roman empire in 180 ad
Trade and moving the roman army around were the two principle reasons for building roads. Ap world history notes visual; Roman trade routes map (orbis, stanford uni) in addition to the 80,000 kilometres of first class roads (as at c. The syrian desert, which would have seriously affected the trade routes. Trade routes of the roman empire in 180 ad The romans were able to establish trade routes throughout europe, asia, and africa. Roman trade routes goods were continually transported throughout the roman empire. All roads lead to rome. This layer has been viewed 31477 time(s) by 24708 user(s). The roman empire, the parthian empire, the kushan empire, the nomadic confederation of the xiongnu, and the han empire.although travel was arduous and knowledge of geography imperfect, numerous contacts were forged as these empires expanded—spreading ideas, beliefs, and. Trade ports during early roman empire, 2nd century a.d., the commercial routes between the mediterranean basin and south asia consisted of wide and complex networks. Romans were businessmen and the longevity of their empire was due to their commercial trade. By the end of the first century b.c., there was a great expansion of international trade involving five contiguous powers:
Komentar
Posting Komentar